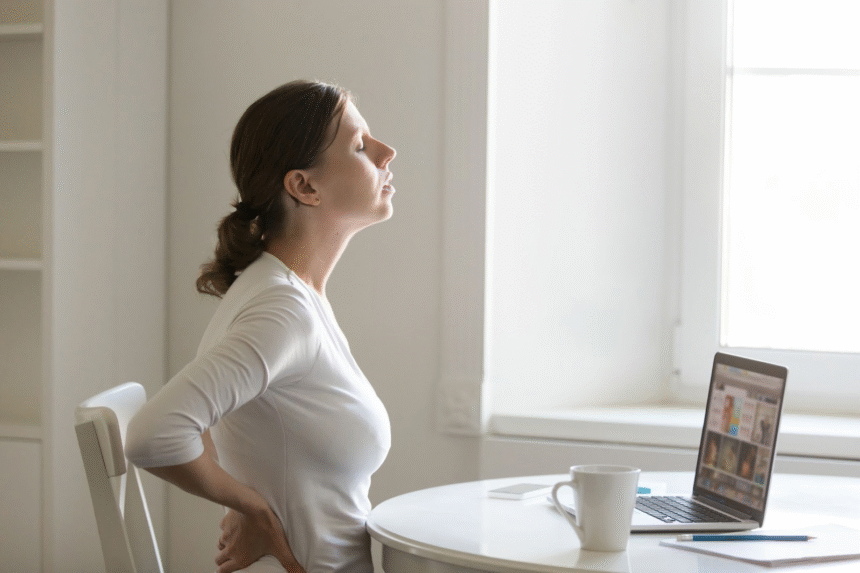
Managing chronic pain without medication is possible through lifestyle changes, therapies, and alternative approaches. These methods help reduce discomfort, improve function, and enhance quality of life while minimizing potential side effects associated with long-term medication use.
Engaging in Regular Exercise
Exercise strengthens muscles, improves flexibility, and supports joint health, which can alleviate chronic pain. Low-impact activities like swimming, walking, and yoga reduce stress on affected areas and improve overall mobility.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy focuses on targeted exercises, posture correction, and movement techniques to manage pain. Therapists create individualized plans that address the root cause of pain while promoting safe activity and preventing further injury.
Mindfulness and Meditation
Mindfulness practices and meditation help individuals manage the emotional and psychological aspects of chronic pain. By focusing on the present moment and regulating breathing, pain perception can be reduced significantly.
Heat and Cold Treatments
Applying heat or cold to painful areas offers temporary relief. Heat relaxes tight muscles and increases blood flow, while cold reduces inflammation and numbs discomfort. Alternating between both can provide effective pain management.
Acupuncture
Acupuncture involves stimulating specific points on the body to relieve pain. Many people find relief from conditions such as back pain, arthritis, and migraines through this traditional therapy.
Massage Therapy
Massage therapy helps relax muscles, improve circulation, and reduce tension. Regular sessions can alleviate pain, enhance flexibility, and support mental relaxation.
Maintaining a Healthy Lifestyle
Healthy habits such as proper nutrition, adequate sleep, and stress management contribute to pain reduction. Avoiding activities that worsen pain and maintaining a healthy weight reduces strain on joints and muscles.
Ergonomic Adjustments
Using ergonomic furniture, supportive footwear, and proper body mechanics can prevent additional strain. Adjusting daily activities to reduce pressure on painful areas supports long-term pain management.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
CBT helps individuals develop coping strategies for chronic pain. By changing negative thought patterns and responses to pain, CBT improves emotional resilience and reduces perceived pain intensity.
Education and Self-Care
Learning about the causes and triggers of pain empowers individuals to take proactive steps. Self-care routines, including stretching, posture correction, and pacing activities, help manage pain effectively without medication.
Conclusion
Chronic pain can be managed safely without relying solely on medication. Exercise, physical therapy, mindfulness, alternative therapies, lifestyle changes, and self-care strategies provide effective pain relief and improve overall quality of life. Combining multiple approaches ensures a holistic and sustainable method for long-term pain management.