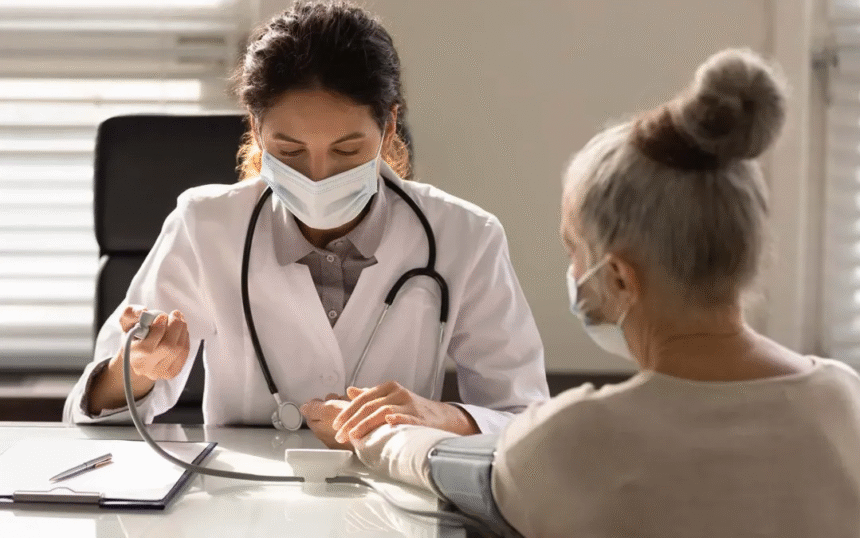
Regular gynecological checkups are essential for maintaining women’s reproductive health and detecting potential problems early. Many women visit a gynecologist only when experiencing symptoms, but preventive care plays a critical role in overall health. Understanding the recommended frequency of visits ensures timely screenings and better health outcomes.
Initial Gynecological Visit
The first gynecological visit is usually recommended between the ages of 13 and 15, or when a girl becomes sexually active. Early visits help educate young women about menstrual health, sexual health, and reproductive care. This foundation encourages lifelong health habits.
Annual Checkups for Adults
For most adult women, visiting a gynecologist once a year is recommended. Annual exams include pelvic exams, breast exams, and discussions about menstrual health, contraception, and sexual health. Routine visits allow early detection of issues such as infections, hormonal imbalances, and other gynecological conditions.
Pap Smears and Cervical Cancer Screening
Pap smears are essential for detecting cervical cancer and precancerous changes. Women aged 21 to 29 should have a Pap smear every three years, while women aged 30 to 65 may combine Pap tests with HPV testing every five years. These screenings significantly reduce the risk of cervical cancer.
Mammogram and Breast Health
Women over the age of 40 are generally advised to have a mammogram every one to two years to detect breast cancer early. Regular breast exams by a gynecologist or self-exams at home help monitor any unusual changes in breast tissue.
Women with Risk Factors
Women with a family history of reproductive cancers, hormonal disorders, or chronic illnesses may require more frequent checkups. Personalized care plans ensure early detection and management of health risks.
Pregnancy and Preconception Care
Women planning pregnancy or who are pregnant should have specialized gynecological visits. Preconception care helps ensure maternal and fetal health, while prenatal checkups monitor pregnancy progress and address potential complications.
Postmenopausal Women
After menopause, women should continue regular gynecological visits to monitor bone health, cardiovascular health, and hormone-related changes. Annual exams remain important for screening and preventive care.
Importance of Open Communication
Regular visits provide an opportunity for women to discuss concerns openly with their gynecologist. Questions about contraception, menstrual irregularities, sexual health, or menopausal symptoms should be addressed during these appointments.
Preventive Health Benefits
Regular gynecological checkups help detect infections, abnormal growths, and early signs of cancer. Preventive screenings improve treatment outcomes and reduce long-term health risks.
Building Lifelong Health Habits
Consistent gynecological care fosters awareness and responsibility for reproductive health. Women who prioritize regular checkups are more likely to maintain overall well-being and prevent complications.
Conclusion
Women should have regular gynecological checkups to maintain reproductive and overall health. Annual visits, routine screenings, and personalized care plans help detect problems early and promote long-term wellness. Prioritizing gynecological health is essential for a healthy and fulfilling life.